Dating apps have become a lucrative business in the digital age, capitalizing on the universal desire for companionship and connection. Behind the scenes, these platforms employ a variety of business models and revenue streams to sustain their operations and generate profits. In this article, we delve into the economics of dating apps, analyzing the different monetization strategies employed by industry leaders and the impact they have on users and the dating landscape.
1. Subscription-Based Models:
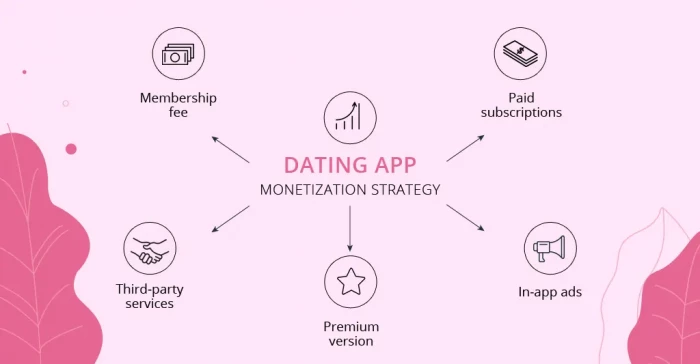
Subscription-based models are a common monetization strategy employed by dating apps, where users pay a recurring fee to access premium features and services. These features may include advanced search filters, unlimited swipes, ad-free browsing, and enhanced privacy settings. By offering subscription tiers at different price points, dating apps can cater to users with varying budgets and preferences while generating predictable recurring revenue.
Subscription-Based Models have emerged as a prevalent revenue strategy in the dating app industry. These models offer users access to premium features and services in exchange for a recurring fee. With Subscription-Based Models, users can unlock advanced functionalities such as unlimited swipes, ad-free browsing, and enhanced privacy settings, enhancing their overall experience on the platform. Dating apps often offer multiple subscription tiers, catering to users with varying budgets and preferences. By leveraging Subscription-Based Models, dating apps can generate predictable recurring revenue while providing users with a customizable and value-added experience, essential elements in the development of successful platforms like Tinder.
2. In-App Purchases:
In-app purchases allow dating app users to unlock additional features or virtual goods through one-time purchases. These may include virtual gifts, profile boosts, or access to exclusive events or matchmaking services. In-app purchases provide users with a sense of exclusivity and customization while offering dating apps an additional revenue stream beyond subscription fees. In-app purchases play a pivotal role in driving revenue and enriching the user experience within mobile applications. By offering users the option to purchase virtual goods, premium features, or exclusive content directly within the app, developers can unlock additional monetization opportunities and provide users with personalized enhancements tailored to their preferences. Whether it's unlocking advanced functionalities, accessing exclusive content, or customizing their digital experience, in-app purchases empower users to personalize their app usage while offering developers a sustainable revenue stream. This dual benefit makes in-app purchases a valuable strategy for developers seeking to optimize both user satisfaction and financial performance.
3. Advertising:
Advertising is another significant revenue stream for many dating apps, particularly those with large user bases and high engagement levels. Dating apps can display targeted advertisements to users based on their demographics, interests, and browsing behavior, allowing advertisers to reach highly relevant audiences. While advertising can generate substantial revenue, dating apps must strike a balance between monetization and user experience to avoid alienating users with intrusive or irrelevant ads. Advertising serves as an integral component of dating app monetization strategies, leveraging user data and engagement metrics to deliver targeted advertisements. Through strategic placement within the app interface, advertisers can reach a highly relevant audience based on demographic information, interests, and browsing behavior. From sponsored profiles to in-app banners and native ad placements, dating apps offer various advertising opportunities to brands seeking to connect with potential customers. While advertising revenue contributes to the overall profitability of dating apps, maintaining a balance between monetization and user experience is essential to ensure user satisfaction and retention in this competitive market landscape.
4. Premium Features:
Premium features represent additional functionalities or enhancements that users can unlock through one-time purchases or subscription upgrades. These features may include advanced matchmaking algorithms, profile verification badges, message read receipts, or access to exclusive events or communities. By offering premium features, dating apps can incentivize users to upgrade their accounts while providing additional value and differentiation in a competitive market, which is crucial when aiming to develop an app like Tinder. Premium features go beyond standard offerings, elevating the user experience and driving revenue growth for dating apps. These advanced functionalities, available through one-time purchases or subscription upgrades, include sophisticated matchmaking algorithms, ensuring more compatible matches. Profile verification badges boost trust and authenticity, while message read receipts enhance communication transparency. Access to exclusive events and communities fosters a sense of belonging, encouraging user engagement and retention. By strategically implementing premium features, dating apps not only enrich the user experience but also create additional value propositions, setting themselves apart in a competitive market landscape.
5. Hybrid Models:
Many dating apps employ hybrid monetization models that combine multiple revenue streams to maximize profitability and cater to diverse user preferences. For example, a dating app may offer both subscription-based premium memberships and in-app purchases for virtual goods or exclusive features. By diversifying their revenue streams, dating apps can reduce reliance on any single source of income and adapt to changing market conditions. In the dynamic landscape of dating app monetization, hybrid models emerge as a strategic approach to balancing profitability and user satisfaction. By integrating various revenue streams such as subscription-based models, in-app purchases, and advertising, dating apps can diversify their income sources while offering users flexibility and choice. This hybrid approach allows dating platforms to cater to diverse user preferences and financial capabilities, driving sustained growth and competitiveness in the market. Moreover, hybrid models enable dating apps to adapt to evolving market trends and consumer behaviors, ensuring long-term viability and success in the ever-changing digital dating landscape.
conclusion
In conclusion, the business of love encompasses a wide range of monetization strategies and revenue streams employed by dating apps to sustain their operations and drive profitability. By offering subscription-based models, in-app purchases, advertising, premium features, and hybrid monetization models, dating apps can cater to diverse user preferences while generating sustainable revenue streams. However, success in the competitive dating app market requires striking a balance between monetization and user experience, ensuring that users feel valued and engaged while pursuing meaningful connections in the digital age. hybrid models are pivotal in the monetization strategies of dating apps, providing a flexible and diversified approach to generating revenue while enhancing user experience. By effectively implementing hybrid models, dating platforms can strike a balance between profitability and user satisfaction, fostering sustained growth and competitiveness in the industry.










