Explore our 3D Printing archive to see how we transform digital designs into high-precision, functional prototypes and components. This section highlights our expertise in additive manufacturing, utilizing advanced printing techniques to create intricate, durable, and customized parts for diverse industries.
3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering an innovative approach to product development, rapid prototyping, and mass customization. As industries increasingly embrace additive manufacturing, the demand for precision, efficiency, and flexibility in production has grown exponentially.
This article explores 3D printing technologies, their applications, advantages, and how XC Machining delivers high-quality 3D-printed components for various industries.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that enables the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, allowing for greater design flexibility and minimal material wastage.
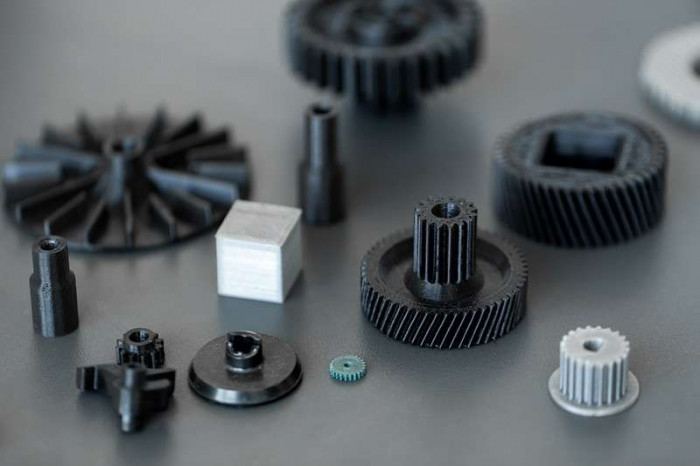

How 3D Printing Works
The 3D printing process begins with computer-aided design (CAD) software, where engineers and designers create digital models of the desired component. This model is then sliced into thin layers, and the 3D printer deposits material—such as plastic, resin, metal, or composite materials—layer by layer until the object is fully formed.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies
1. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is one of the most common and cost-effective 3D printing technologies. It works by melting thermoplastic filaments and depositing them layer by layer through a heated nozzle.
- Materials Used: PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon, TPU
- Applications: Prototyping, tooling, functional parts, and consumer products
- Advantages: Affordable, easy to use, and widely available
2. Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA is a high-resolution 3D printing technology that uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers. It is ideal for intricate, smooth, and highly detailed parts.
- Materials Used: Photopolymer resins (standard, tough, flexible, biocompatible)
- Applications: Medical models, dental prosthetics, jewelry, and engineering prototypes
- Advantages: High precision, smooth surface finish, excellent detail
3. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS uses a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, creating durable and functional parts without support structures. It is commonly used in industrial applications.
- Materials Used: Nylon, polyamide, TPU, carbon-fiber composites
- Applications: Aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial manufacturing
- Advantages: Strong, flexible, and heat-resistant parts; no support structures needed
4. Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
MJF is an industrial-grade 3D printing method that uses fine powder and a fusing agent, which is then exposed to heat to form high-strength parts.
- Materials Used: Nylon, TPU, composite powders
- Applications: Functional prototypes, aerospace, medical, and electronic enclosures
- Advantages: Faster production, high detail resolution, and excellent mechanical properties
5. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA, DLP uses a digital light projector to cure liquid resin. The key difference is that DLP can cure an entire layer at once, making it faster than SLA.
- Materials Used: Photopolymers, flexible and high-temperature resins
- Applications: Dental, jewelry, consumer goods, and engineering
- Advantages: High speed, fine details, and smooth surfaces
Applications of 3D Printing Across Industries
1. Aerospace & Automotive
- Lightweight, durable parts for aircraft and vehicle interiors
- Rapid prototyping for new designs and testing
- Heat-resistant and functional components for engines and structures
2. Medical & Healthcare
- Custom prosthetics and orthopedic implants tailored to patient needs
- 3D-printed surgical models for pre-operative planning
- Bioprinting for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine research
3. Manufacturing & Engineering
- Rapid prototyping to test and refine product designs
- Custom tooling, jigs, and fixtures for assembly lines
- End-use parts for industrial applications
4. Consumer Goods & Electronics
- Wearable technology with customized ergonomic designs
- Custom enclosures and cases for electronic devices
- Fashion and jewelry prototyping with intricate designs
5. Education & Research
- 3D-printed learning aids for STEM education
- Architectural models and mechanical prototypes
- Research in material science and innovation
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing has gained widespread adoption across multiple industries, including:
Aerospace & Automotive – Lightweight and complex parts for enhanced performance.
Medical & Healthcare – Custom prosthetics, dental implants, and medical devices.
Consumer Products – Customized jewelry, fashion accessories, and home décor.
Manufacturing & Prototyping – Rapid prototyping for product development, reducing time-to-market.
Advantages of 3D Printing
Cost-Effective Production – Reduces material waste and lowers manufacturing costs.
Customization & Flexibility – Designs can be modified quickly without expensive tooling.
Faster Prototyping – Enables rapid product development and testing.
Complex Geometries – Capable of producing intricate and highly detailed components.
Advantages of 3D Printing
1. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
3D printing reduces material waste and eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling, making it a cost-efficient production method.
2. Design Flexibility
Unlike traditional manufacturing, complex geometries and intricate details can be easily printed without additional processes.
3. Customization & Personalization
3D printing enables one-off production runs with unique designs tailored to specific requirements.
4. Faster Time-to-Market
Companies can develop prototypes and final products much faster, allowing for quick testing, revisions, and deployment.
5. Lightweight & Strong Materials
Many 3D printing materials are lightweight yet durable, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
Why Choose XC Machining for 3D Printing?
At XC Machining, we provide industry-leading 3D printing solutions using advanced FDM, SLA, SLS, and MJF technologies. Our expertise ensures high-quality, precision-engineered components tailored to meet the needs of automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors.
Conclusion
3D printing continues to reshape industries by enabling faster, more efficient, and cost-effective manufacturing. Whether you're looking for functional prototypes, end-use parts, or highly customized designs, XC Machining provides expert 3D printing services tailored to your needs.
By leveraging cutting-edge additive manufacturing technologies, businesses can streamline production, reduce costs, and bring innovative products to market faster than ever before.
Contact XC Machining today to explore how our advanced 3D printing solutions can enhance your manufacturing and product development processes.
Why Choose XC Machining for 3D Printing?
At XC Machining, we specialize in CNC Machining, custom die-cutting, and injection molding, delivering high-quality, precision-engineered parts. Our 3D printing services offer rapid prototyping and custom manufacturing solutions, ensuring efficient production with exceptional accuracy and durability.
Our Capabilities Include:
✅ Rapid Prototyping – Bring your designs to life with fast turnaround times
✅ Custom Manufacturing – Tailor-made solutions for specialized applications
✅ High-Quality Materials – Choose from thermoplastics, resins, nylons, and composites
✅ Scalable Production – From small-batch prototypes to full-scale manufacturing
With state-of-the-art machinery, expert engineers, and a commitment to excellence, we ensure every 3D-printed component meets the highest standards of precision and durability.
📞 Phone No: 13728121373
📍 Location: UCC, Nancheng Street, DongGuan, China
📧 Email: [email protected]