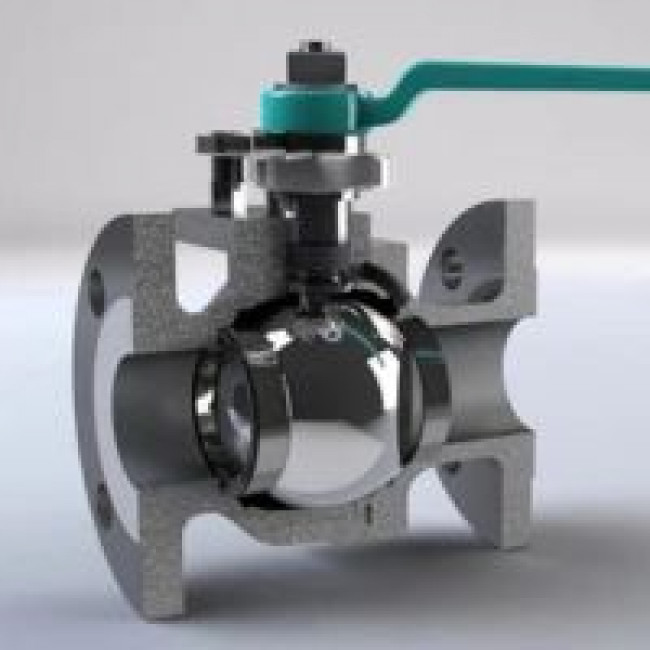
Control valves are an essential component of many industrial processes that involve the regulation of fluid flow, pressure, or temperature. They are used to control the flow of liquids, gases, and steam in pipelines, and they are essential for maintaining the stability and safety of the process. However, like any other mechanical device, control valve have their limitations, and it is essential to understand these limitations to optimize their performance and reliability. In this article, we will discuss some of the limitations of control valves.
Limited Accuracy Control valves are designed to regulate the flow of fluids and gases through a pipeline, but they are not always accurate. They may not precisely control the flow rate or the pressure due to various factors like friction, turbulence, and variations in the fluid's viscosity or density. Hence, there may be slight deviations in the valve's output, leading to the inaccuracy of the overall process.
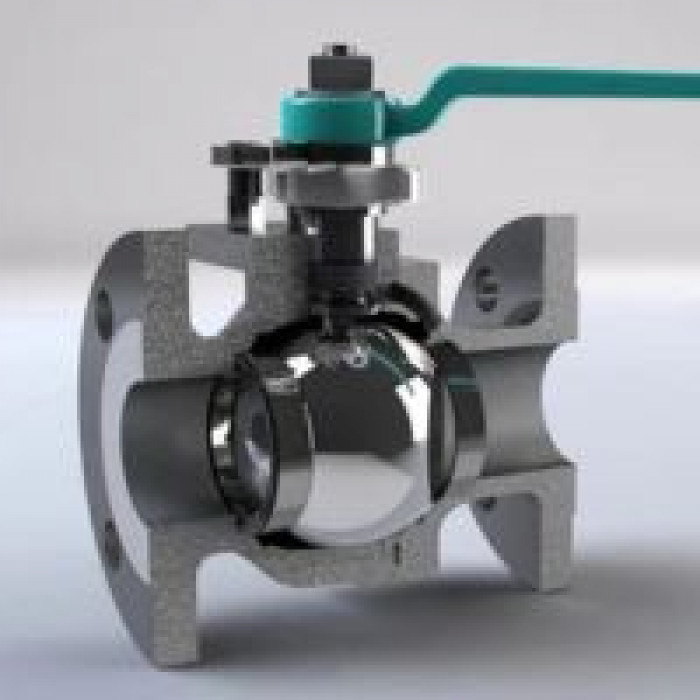

Limited Rangeability The rangeability of a control valve is defined as the ratio of its maximum to minimum controllable flow rate. Most control valves have limited rangeability, which means they can only control the flow of fluids within a specific range. If the flow rate falls outside this range, the valve will not function correctly, leading to fluctuations in the process. This limitation can be addressed by selecting the right control valve with suitable rangeability.
Limited Response Time Control valves have a certain response time, which is the time taken by the valve to respond to a change in the control signal. This response time is influenced by various factors like the valve's size, design, and actuation mechanism. Slow response time can lead to delays in the process, which can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
Limited Operating Temperature and Pressure Control valves have limits on the maximum temperature and pressure they can operate at. If these limits are exceeded, the valve's components may fail, leading to leakage or valve failure. This limitation can be addressed by selecting control valves with appropriate materials and construction to handle high temperatures and pressures.
Limited Reliability Control valves can fail due to various reasons like corrosion, erosion, mechanical wear and tear, and clogging. Valve failure can lead to disruptions in the process, resulting in downtime, loss of productivity, and safety hazards. To mitigate this limitation, regular maintenance and inspection are necessary to ensure that the valves are functioning correctly.
In conclusion, control valves are essential components of industrial processes, but they have their limitations. The accuracy, rangeability, response time, operating temperature and pressure, and reliability of control valves are factors that need to be considered while selecting and operating them. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance can help to optimize their performance and reliability, leading to efficient and safe operations.
Control valves are an essential component of many industrial processes that involve the regulation of fluid flow, pressure, or temperature. They are used to control the flow of liquids, gases, and steam in pipelines, and they are essential for maintaining the stability and safety of the process. However, like any other mechanical device, control valves have their limitations, and it is essential to understand these limitations to optimize their performance and reliability. In this article, we will discuss some of the limitations of control valves.
Limited Accuracy Control valves are designed to regulate the flow of fluids and gases through a pipeline, but they are not always accurate. They may not precisely control the flow rate or the pressure due to various factors like friction, turbulence, and variations in the fluid's viscosity or density. Hence, there may be slight deviations in the valve's output, leading to the inaccuracy of the overall process.
Limited Rangeability The rangeability of a control valve is defined as the ratio of its maximum to minimum controllable flow rate. Most control valves have limited rangeability, which means they can only control the flow of fluids within a specific range. If the flow rate falls outside this range, the valve will not function correctly, leading to fluctuations in the process. This limitation can be addressed by selecting the right control valve with suitable rangeability.
Limited Response Time Control valves have a certain response time, which is the time taken by the valve to respond to a change in the control signal. This response time is influenced by various factors like the valve's size, design, and actuation mechanism. Slow response time can lead to delays in the process, which can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
Limited Operating Temperature and Pressure Control valves have limits on the maximum temperature and pressure they can operate at. If these limits are exceeded, the valve's components may fail, leading to leakage or valve failure. This limitation can be addressed by selecting control valves with appropriate materials and construction to handle high temperatures and pressures.
Limited Reliability Control valves can fail due to various reasons like corrosion, erosion, mechanical wear and tear, and clogging. Valve failure can lead to disruptions in the process, resulting in downtime, loss of productivity, and safety hazards. To mitigate this limitation, regular maintenance and inspection are necessary to ensure that the valves are functioning correctly.
In conclusion, control valves are essential components of industrial processes, but they have their limitations. The accuracy, rangeability, response time, operating temperature and pressure, and reliability of control valves are factors that need to be considered while selecting and operating them. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance can help to optimize their performance and reliability, leading to efficient and safe operations.
Control valves are widely used in the process industries to regulate the flow of fluids, gases, and steam in pipelines. They are critical components that ensure the stability, efficiency, and safety of the process. However, control valves have limitations that can impact their performance and reliability. It is crucial to understand these limitations to optimize the valve's performance and ensure safe and efficient operation. In this article, we will discuss the limitations of control valves in detail.
- Limited Accuracy Control valves are designed to control the flow of fluids through a pipeline, but they are not always accurate. Several factors can impact the valve's accuracy, including friction, turbulence, and variations in the fluid's viscosity or density. Additionally, the accuracy of the valve can be influenced by the valve's design, construction, and actuation mechanism.
The accuracy of a control valve is typically expressed in terms of the valve's deviation from the setpoint. The deviation is the difference between the actual valve output and the desired setpoint. The deviation can be positive or negative, and it can impact the overall process's stability and performance. Even small deviations can cause fluctuations in the process, leading to product quality issues or safety hazards.
To mitigate the impact of accuracy limitations, it is essential to select the appropriate control valve for the application. The valve's design, materials, and actuation mechanism should be chosen to ensure the valve's accuracy under the expected operating conditions.
- Limited Rangeability Rangeability is the ratio of the maximum controllable flow rate to the minimum controllable flow rate. For example, a valve with a rangeability of 10:1 can control the flow rate from 10% to 100% of its maximum flow rate. Rangeability is an important factor in the valve's performance because it determines the valve's ability to control the flow rate accurately.
Most control valves have limited rangeability, which means they can only control the flow of fluids within a specific range. If the flow rate falls outside this range, the valve will not function correctly, leading to fluctuations in the process. Additionally, the valve's accuracy can be affected when operating at the extremes of its rangeability.
To mitigate the impact of rangeability limitations, it is essential to select the appropriate control valve for the application. The valve's rangeability should be chosen based on the expected range of flow rates, and the valve's accuracy should be evaluated at the extremes of its rangeability.
- Limited Response Time Response time is the time taken by the valve to respond to a change in the control signal. The response time is influenced by several factors, including the valve's size, design, and actuation mechanism. Slow response time can lead to delays in the process, which can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the system.
The response time of the valve can be influenced by the valve's construction and materials. For example, valves with a large actuator volume can have slower response times than valves with a smaller actuator volume. Additionally, the type of actuation mechanism used, such as pneumatic or electric, can impact the valve's response time.
To mitigate the impact of response time limitations, it is essential to select the appropriate control valve for the application. The valve's response time should be evaluated under the expected operating conditions, and the valve's construction and materials should be chosen to optimize its response time.
- Limited Operating Temperature and Pressure Control valves have limits on the maximum temperature and pressure they can operate at. If these limits are exceeded, the valve's components may fail, leading to leakage or valve failure. The valve's operating temperature and pressure limits are influenced by several factors, including the valve's construction and materials.